Explain the Difference Between a Bound Orbit and Unbound Orbit
Gravity causes objects in space that have mass to be attracted to other nearby objects. Bound orbits are unstable within a certain region r 3 r s orbits can intrinsically decay due to gravitational radiation.
Chapter 4 In 4th Edition Of Bennett Et Al
An orbit is the curved path that an object in space such as a star planet moon asteroid or spacecraft takes around another object due to gravity.

. What is the difference between a bound orbit and an unbound orbit around the Sun. 16 What is the difference between a bound orbit and an unbound orbit around the Sun. Describe the difference between a bound orbit and an unbound orbit.
Explain the difference between weight and mass. What can you say about the future of these two objects. Describe the difference between a bound orbit and an unbound orbit.
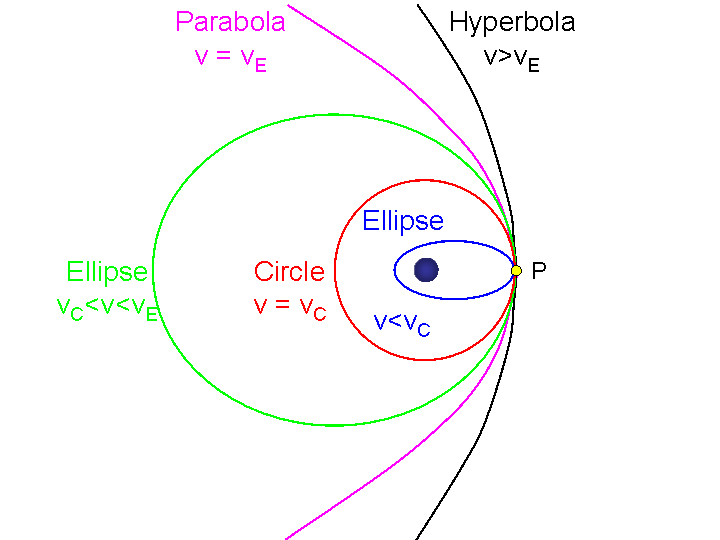
Differences between speed velocity acceleration Speed distance travelled time required speed d t. An unbound orbit is one in which the light object is gravitationally attracted toward the heavier object but the attraction is not strong enough to cause the light objects path to bend enough for it to make full loops around the. An object on a bound orbit follows the same path around the Sun over and over while an object on an unbound orbit.
For example the planets are in bound orbits around the Sun. Explain the difference between weight and mass. Orbits are bound and objects are trapped in orbit forever around the parent body.
B An object on a bound orbit has a gravitational attraction to the Sun while an object on an unbound orbit does not. Each circular orbit has a characteristic circular velocity. We know this version has to be only valid for bound orbits for two reasons.
And two for an unbound orbit a defined using the distance r_rm max doesnt exist. Tides at the Bay of Fundy You Tube looped So far weve talked about SunEarthmoonetc as if they were completely rigid. B An object on a bound orbit has a gravitational attraction to the Sun while an object on an unbound orbit does not.
C A bound orbit is circular while an unbound orbit is elliptical. Orbits become unbound when the object reaches escape velocity. In quantum physics you can solve for the allowable energy states of a particle whether it is bound or trapped in a potential well or is unbound having the energy to escape.
Problem 38 Two objects are leaving the vicinity of the Sun one traveling in a bound orbit and the other in an unbound orbit. A bound orbit is an orbit allowed by the universal law of gravitation and an unbound orbit is not. Prefixes and suffixes are two types of bound morphemes.
What happened is that as I got the orbital parameters closer and closer to the critical point between the orbit being bound vs. A A bound orbit is an orbit allowed by the universal law of gravitation and an unbound orbit is not. Bound orbits are generally stable.
The force of gravity is propor-tional to the mass of each object and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Calculate the speed at which Neptune plods along in its orbit. Take a look at the potential in the following figure.
Here r s is a length-scale associated with the mass of a black hole called the Schwarzschild radius. What is the difference between a bound and an unbound orbit. A bound orbit will repeat itself.
Inflectional morphemes and derivational morphemes. 24 _____ AA bound orbit is an orbit allowed by the universal law of gravitation and an unbound orbit is not. Describe the difference between a bound.
What is the difference between a bound orbit and an unbound orbit around the Sun. Unbound with non-circular starting parameters the orbit would first drop into an approximately-circular orbit before then dropping into a highly-eccentric orbit or separating. An object on a bound orbit follows the same path around the Sun over and over while an object on an unbound orbit approaches the Sun just once and then never returns.
Go from a bound orbit to an unbound orbit TIDES. 34 Planets orbit the Sun in bound elliptical orbits because of gravity. D An object on a bound orbit follows the same path.
Earth speeds along at 298 k m s in its orbit. An unbound orbit never returns Suppose astronomers discovered an object approaching the Sun in an unbound orbit. If this attraction brings them together with enough momentum they can sometimes begin to orbit each other.
Neptunes nearly circular orbit has a radius of 45 10 9 k m and the planet takes 1648 years to make one trip around the Sun. A bound orbit is one in which the light object makes many loops around the heavier object. A A bound orbit is an orbit allowed by the universal law of gravitation and an unbound orbit is not.
The dip or well in the potential means that particles can be trapped in it if they dont have too much energy. Which of these orbits you will be in is determined by your orbital speed. 24What is the difference between a bound orbit and an unbound orbit around the Sun.
Parabolas which are a special case of a hyperbola Orbits are unbound and objects can escape the gravity of the parent body. Bound morphemes have no linguistic meaning unless they are connected to a root or base word or in some cases another bound morpheme. Under what conditions can we use Newtons version of Keplers third law to calculate an objects mass and what quantities must we measure in order to complete the calculation.
A bound orbit is circular while an unbound orbit is elliptical A bound orbit is circular while an unbound orbit is elliptical. One since gamma and a are both positive this formula always gives a negative energy. BAn object on a bound orbit has a gravitational attraction to the Sun while an object on an unbound orbit does not.
Depending on how they modify a root word bound morphemes can be grouped into two categories.

Unbound Orbits And Orbital Energy

Unbound Orbits And Orbital Energy
No comments for "Explain the Difference Between a Bound Orbit and Unbound Orbit"
Post a Comment